Experiencing hair loss can be quite distressing, particularly when the reasons behind it are unclear. It’s more than just a cosmetic concern; it can have a significant impact on your self-esteem and overall health. The silver lining? Figuring out the cause is the crucial first step toward finding a remedy. Let’s take a look at the top 10 reasons for hair loss.
What is Hair Loss?

Hair loss is characterized by the excessive loss or thinning of hair from the scalp or other areas of the body. While losing between 50 to 100 hairs a day is considered normal, noticeable thinning may signal a deeper issue.
This is a widespread issue that can affect people of all ages and genders. Known as alopecia, hair loss can greatly influence one’s self-image and quality of life. It’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and available treatments to effectively manage and possibly reverse hair loss.
Symptoms of Hair Loss
There are many symptoms, including:
- Gradual Thinning on the Scalp: This is often seen in older adults, particularly those with androgenetic alopecia.
- Patchy or Circular Bald Spots: These can emerge suddenly and may affect the scalp, beard, or eyebrows.
- Sudden losing hair: Hair may come out in clumps during washing or brushing, often due to physical or emotional stress.
- Complete loss of hair: This can occur as a result of medical treatments such as chemotherapy.
- Scaly Patches or Redness: These symptoms may indicate fungal infections like ringworm.
Causes of Hair Loss
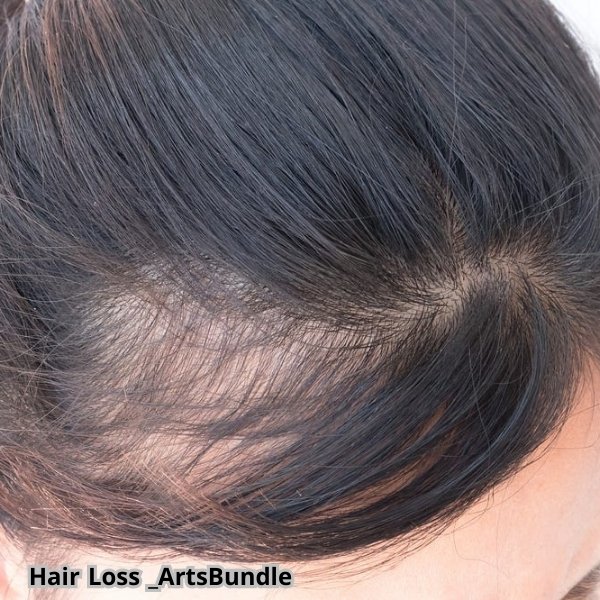
There are 10 common causes of n losing hair, including:
1. Genetic Factors (Androgenetic Alopecia)
If losing hair is common in your family, you may be experiencing androgenetic alopecia, often referred to as male or female pattern baldness. This hereditary condition impacts hair follicles, resulting in gradual thinning and eventual loss of hair. In men, it typically begins with a receding hairline, while women tend to notice overall thinning. Conditions like male-pattern and female-pattern baldness are the most prevalent causes, often linked to hormonal changes and aging.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormones significantly influence hair health. Life events such as pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can lead to hormonal fluctuations that may result in hair loss. Additionally, conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can interfere with hair growth, causing thinning or shedding. Changes during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid issues can disrupt the natural hair growth cycle.
3. Nutritional Deficiencies
For your hair to flourish, it requires adequate nutrition. Lacking essential vitamins like biotin, iron, and zinc can weaken hair strands, leading to increased hair fall. Maintaining a balanced diet filled with leafy greens, nuts, and lean proteins can greatly benefit your hair health. Insufficient intake of iron, protein, or other vital nutrients can worsen the loss of hair.
4. Stress and Hair Loss (Telogen Effluvium)
Have you noticed more hair falling out after a stressful situation? This phenomenon is known as telogen effluvium, a temporary condition where stress causes hair to enter the shedding phase. Physical stress from surgeries or illnesses can also contribute to losing hair. Both emotional and physical stress can push hair follicles into a resting phase, resulting in noticeable shedding.
5. Medical Conditions
Various health issues can negatively impact your hair. For instance, thyroid disorders can disrupt hair growth cycles, while autoimmune diseases like alopecia areata cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to patchy and lost hair. Conditions such as alopecia areata, infections like ringworm, or underlying illnesses such as lupus can all contribute to losing hair.
6. Medications and Treatments
Certain medications can lead to losing hair as a side effect. This includes those prescribed for high blood pressure, depression, and acne. Chemotherapy is another treatment that may result in temporary loss of hair, as it targets rapidly dividing cells, including those in hair follicles. Additionally, medications for cancer, depression, arthritis, and heart conditions can contribute to hair thinning.
7. Hairstyling and Hair Damage
Regularly using heat styling tools, undergoing chemical treatments, and wearing tight hairstyles can gradually weaken your hair. Styles such as braids, buns, or ponytails may lead to traction alopecia, a condition caused by the constant pulling on the hair.
8. Scalp Infections
Infections like ringworm can impact your scalp and result in loss of hair. Common symptoms include redness, itching, and scaly patches. Prompt treatment with antifungal medications can help prevent further damage.
9. Aging and Hair Loss
As we grow older, it’s normal for hair to become thinner and finer. The hair growth cycle slows down, and follicles produce less hair. While aging is a natural process, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help slow down hair thinning.
10. Lifestyle Habits
Unhealthy habits such as smoking and inadequate sleep can negatively affect hair health. Smoking decreases blood circulation to the scalp, while not getting enough sleep hampers the body’s ability to repair and regenerate, including hair cells.
Medical Causes of Hair Loss
losing hair, also referred to as alopecia, affects millions of people around the globe. The reasons behind it can be quite diverse, ranging from temporary issues to long-term health conditions. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment.
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Hair Loss)
This genetic condition is the leading cause of losing hair.
• Characteristics: Gradual thinning of hair, usually starting at the crown for men and spreading across the scalp for women.
• Mechanism: Sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, results in the miniaturization of hair follicles.
• Treatment: Options include minoxidil, finasteride (for men), and hair transplantation.
2. Telogen Effluvium
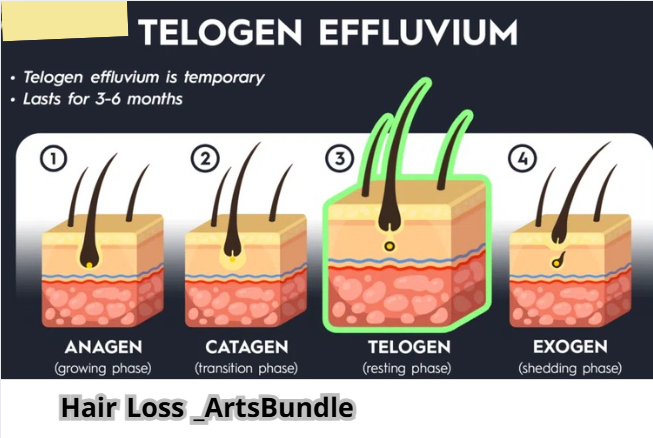
This temporary condition involves hair shedding, often triggered by stress or physical shock.
• Triggers: Events like surgery, childbirth, serious illness, or nutritional deficiencies.
• Symptoms: Widespread hair thinning that typically begins months after the triggering incident.
• Management: Focus on resolving the underlying issues and allow time for hair to regrow.
3. Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
• Presentation: Sudden, circular patches of losing hair on the scalp or other areas of the body.
• Associated Conditions: Often linked with thyroid disorders and vitiligo.
• Treatment Options: Corticosteroids, immunotherapy, and JAK inhibitors.
4. Traction Alopecia
This type of losing hair results from consistent tension on the hair shaft.
• Causes: Tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, and extensions.
• Reversible?: Yes, if caught early and tight hairstyles are avoided.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of essential vitamins and minerals can negatively impact hair health.
• Key Deficiencies:
o Iron: Particularly common in women, leading to losing hair due to anemia.
o Zinc and Vitamin D: Crucial for maintaining healthy hair follicles.
o Protein: Vital for the production of keratin.
• Correction: A balanced diet or supplements, ideally under medical guidance.
6. Hormonal Imbalances
Changes in hormone levels can interfere with the hair growth cycle.
• Common Situations:
o Pregnancy and the postpartum period.
o Menopause.
o Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
• Solution: Hormone therapy or specific medical treatments.
7. Thyroid Disorders
Both underactive and overactive thyroid conditions can contribute to hair thinning.
• How It Works: Changes in metabolism impact the cycling of hair follicles.
• Treatment: Restoring normal thyroid function with medication.
8. Scalp Infections
Infections like ringworm (tinea capitis) can lead to patchy losing hair.
• Signs: Scaly areas, itching, and sometimes pus-filled sores.
• Treatment: Antifungal medications and topical solutions.
9. Medications and Medical Treatments
Some medications and therapies can cause loss of hair as a side effect.
• Examples:
o Chemotherapy and radiation.
o Beta-blockers, antidepressants, and blood thinners.
• Approach: Consider switching medications if feasible or explore hair regrowth options.
10. Trichotillomania
This psychological condition involves the compulsive pulling out of hair.
• Consequences: Irregular bald spots and broken strands.
• Treatment: Cognitive-behavioral therapy and stress management techniques.
11. Cicatricial Alopecia (Scarring Alopecia)
This refers to a set of uncommon conditions that lead to irreversible losing hair.
• Mechanism: Inflammation damages hair follicles, which are then replaced by scar tissue.
• Subtypes: Includes lichen planopilaris and central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA).
• Treatment: Involves anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants.
12. Psoriasis
A long-lasting autoimmune skin condition that impacts the scalp.
• Symptoms: Characterized by thick, scaly patches that may cause temporary losing hair.
• Management: Treated with topical steroids, salicylic acid, and biologic medications.
13. Seborrheic Dermatitis
This condition arises from excessive oil production, leading to scalp inflammation.
• Symptoms: Presents as greasy scales and itching sensations.
• Treatment: Often managed with medicated shampoos that contain ketoconazole or zinc pyrithione.
14. Cancer and Chemotherapy
Cancer treatments frequently result in temporary loss of hair.
• Why?: Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing cells, which includes hair follicles.
• Recovery: Hair usually regrows after the treatment concludes.
15. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
This autoimmune disorder can lead to thinning hair or bald spots.
• Mechanism: Involves inflammation of the scalp along with other systemic impacts.
• Treatment: Managed with immunosuppressive therapies.
16. Diabetes
Poor blood circulation and glucose management can negatively affect hair follicle health.
• Complications: May lead to overall thinning and slower regrowth.
• Prevention: Focus on controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining a balanced diet.
17. Age-Related Hair Thinning
As we age, hair tends to become thinner due to decreased activity in hair follicles.
• Timeline: This effect is usually more noticeable after the age of 50.
• Management: Consider cosmetic treatments and make lifestyle changes to help.
18. Environmental Factors
Elements like pollution, UV rays, and harsh hair products can harm your hair.
• Protection Tips: Use protective hair products, avoid excessive processing, and limit exposure to damaging substances.
Related Article: The Best Hair Loss Treatment for Men in 2024
Preventing Hair Loss

• Maintain a Nutritious Diet: Focus on foods high in iron, biotin, and omega-3 fatty acids.
• Handle Hair with Care: Steer clear of harsh chemicals and limit heat styling.
• Control Stress: Engage in relaxation practices such as yoga or deep breathing.
• Prevention Approaches
While you can’t completely eliminate genetic factors, taking care of your scalp, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet can help slow down or reduce the loss of hair.
Treatments for Hair Loss
There are several ways to treat the loss of hair, these include:
- Topical Solutions: Products such as Minoxidil can help promote hair growth.
- Medications: Finasteride is known to be effective for male pattern baldness.
- Advanced Treatments: For more severe cases, consider options like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy or hair transplants.
1. Over-the-Counter Treatments
• Minoxidil: This FDA-approved solution comes in liquid or foam form and is designed to encourage hair regrowth while slowing down loss of hair.
2. Prescription Treatments
• Finasteride: Often prescribed for men experiencing pattern baldness, it works by reducing the hormonal factors that contribute to loss of hair.
Spironolactone: This is a viable option for women dealing with hormonal-related hair thinning.
3. Non-Medical Strategies
Hair Care Practices: Treating your hair gently, minimizing heat styling, and steering clear of tight hairstyles can help prevent additional damage.
Nutritional Changes: Focus on a diet that includes vital vitamins such as biotin, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids.
4. Advanced Treatment Options
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): This involves injections that activate dormant hair follicles.
Hair Transplants: A surgical method that moves healthy hair follicles to areas experiencing baldness.
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): This technique enhances hair density by boosting blood circulation in the scalp.
Experiencing hair loss can seem overwhelming, but knowing the underlying reasons can help you take proactive steps. By addressing factors ranging from genetics to lifestyle choices, you can work towards rejuvenating your hair’s health and shine.
Can hair loss be reversed?
Depending on the underlying cause. Acting early is crucial.
What is the best diet for hair growth?
A diet high in biotin, iron, and protein promotes healthy hair.
How can I tell if my hair loss is serious?
If you notice excessive or patchy shedding, it’s best to consult a doctor.
Are natural remedies effective for hair loss?
Some remedies, such as coconut oil and aloe vera, may provide benefits, but results can vary.
When should I see a doctor about hair loss?
If your loss of hair continues or gets worse, it’s wise to seek professional help.





